Understanding Blood Sugar Levels and How to Control Them
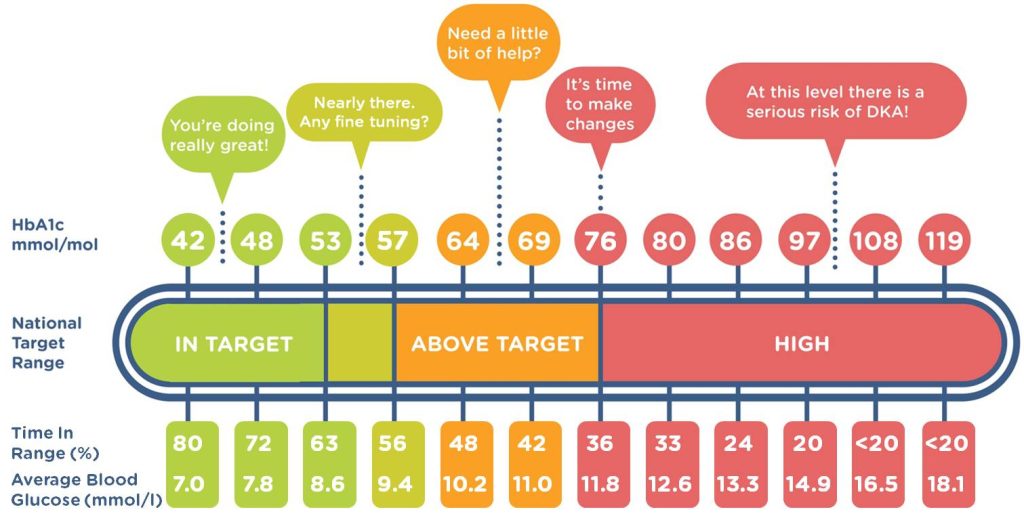
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, or glucose, serves as the primary source of energy for our bodies. However, when levels become too high or too low, it can lead to serious health complications. Let’s delve into what blood sugar levels mean and explore strategies to keep them in check.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels:
Blood sugar levels refer to the concentration of glucose present in the bloodstream at any given time. The body tightly regulates these levels to ensure they remain within a narrow range, typically between 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes. However, this range may vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and time since last meal.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels:
- Diet: Foods high in carbohydrates, especially refined sugars and processed grains, can cause blood sugar levels to spike rapidly.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by muscles.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, are prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
- Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can cause blood sugar levels to rise, especially in people with diabetes.
How to Control Blood Sugar Levels:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the consumption of sugary and processed foods, opting instead for foods with a low glycemic index.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity most days of the week. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercise (such as walking, swimming, or cycling) and strength training to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels, especially if you have diabetes. This helps you understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication for diabetes, take it as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or altering medication regimens without medical supervision can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. Managing stress can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to insulin resistance, affecting blood sugar control.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Dehydration can cause blood sugar levels to rise, so it’s essential to stay well-hydrated.

Conclusion:
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and medication adherence (if applicable), you can effectively manage and control your blood sugar levels. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support in managing your blood sugar levels effectively.
